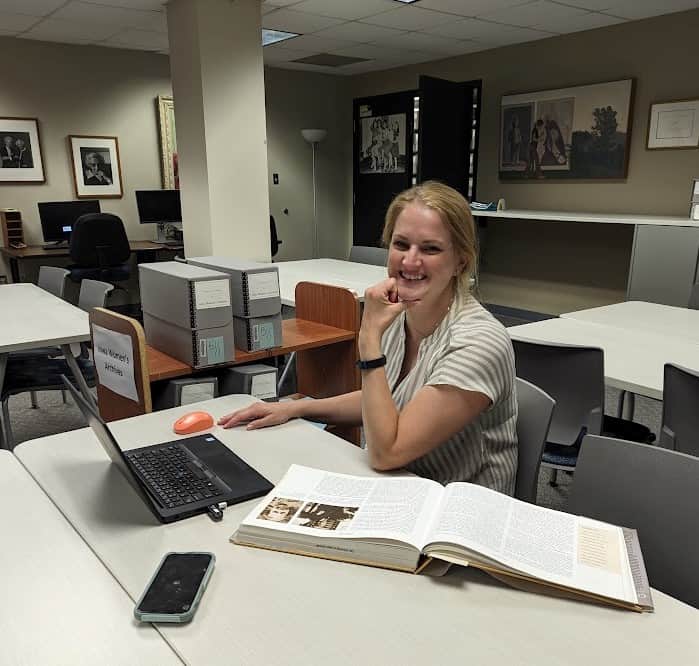
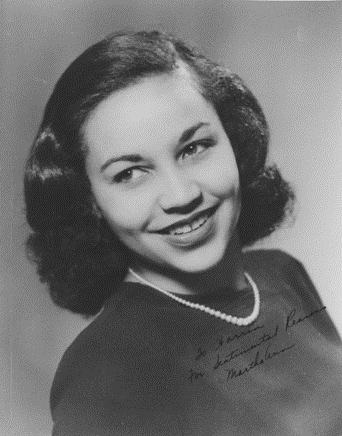Edna Griffin, known as the Rosa Parks of Iowa, has gained deserved attention over the years for her civil rights activism, especially for her role in the effort to desegregate the lunch counter at Katz Drug Store in Des Moines. Her actions resulted in a successful suit against the store under Iowa’s 1884 Civil RightsContinue reading “Kerber Grant Recipient’s Work Will Feature Political Activist Edna Griffin”
Tag Archives: civil rights
Civil Rights Trailblazer June Davis Donates Papers to IWA
This post is by Archives Assistant Heather Cooper. The Iowa Women’s Archives recently received the first installment of a new collection of personal papers from Norma June Wilson Davis. Davis, who later became an administrator at the University of Iowa, was at the forefront of the student civil rights movement in Atlanta, Georgia, in theContinue reading “Civil Rights Trailblazer June Davis Donates Papers to IWA”
Edna Griffin, Civil Rights Activist
This post is the tenth installment in our series highlighting African American history in the collections of the Iowa Women’s Archives. The series ran weekly during Black History Month, and will continue monthly for the remainder of 2020. This past summer, we have seen a nationwide movement for change. In Iowa City, Philadelphia, Chicago, Seattle,Continue reading “Edna Griffin, Civil Rights Activist”
Martha Nash: An Iowa Advocate for Black Voices
This post by IWA Student Specialist, Erik Henderson, is the fourth installment in our series highlighting African American history in the Iowa Women’s Archives collections. The series has run weekly during Black History Month, and will continue monthly for the remainder of 2020. The Martha Ann Furgerson Nash papers are filled with information about herContinue reading “Martha Nash: An Iowa Advocate for Black Voices”