The following is written by Olson Graduate Research Assistant, Kaylee Swinford. Corita Kent was an American artist, educator, activist, and former religious sister. With a rebellious spirit, Corita was a pioneering designer, who produced a body of work for over three decades combining themes of spirituality, hope, peace, and acceptance. Inspired by the popular PopContinue reading “Voices from the stacks: Corita Kent”
Tag Archives: sackner archive
Beauty in Breathing: An Exhibit
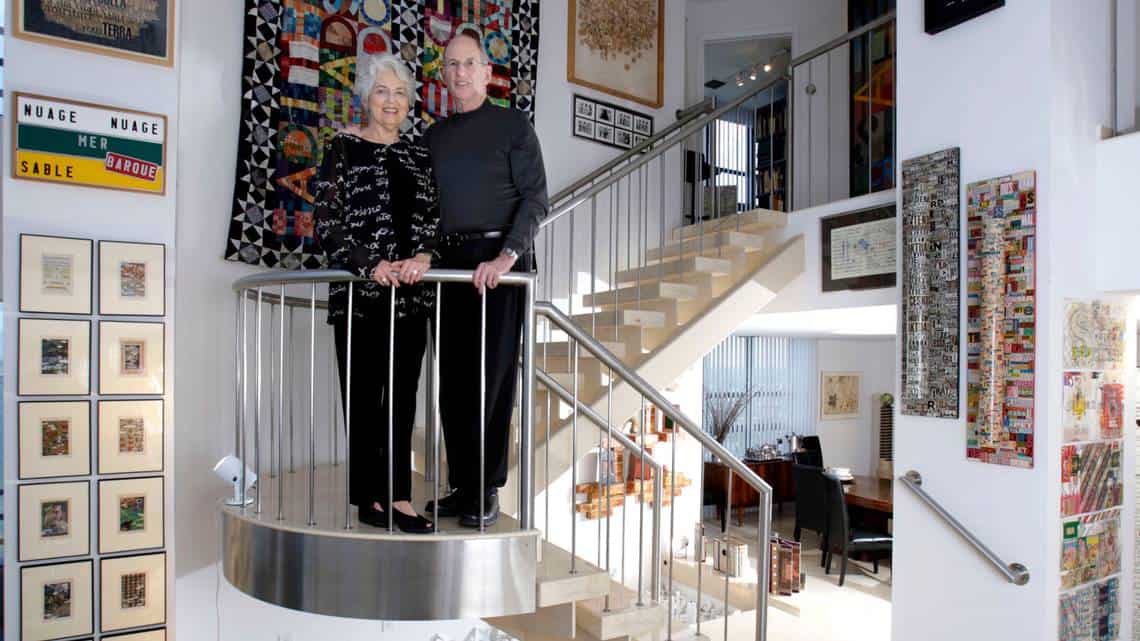
The following was written by Rich Dana, Sackner Archive Project Coordinator Marvin and Ruth Sackner were the world’s foremost collectors of “visual poetry,” artwork that combines visual elements and text. Dr. Sackner was also an internationally respected pulmonologist and inventor of many medical devices. In 1992, the Sackners created a unique exhibition of work byContinue reading “Beauty in Breathing: An Exhibit”
In Memory of Kirby Congdon, an Unsung Hero of American Poetry
The following is written by Rich Dana, Sackner Archive Project Coordinator Librarian On June 3, 98-year-old Kirby Congdon passed away in Key West, Florida, a town that had recognized him as its first poet laureate. Although the arts community of Key West understood the importance of Congdon and his work, much of the rest ofContinue reading “In Memory of Kirby Congdon, an Unsung Hero of American Poetry”
Welcome Rich Dana
We are pleased to announce Rich Dana as Special Collections and Archives’ Sackner Archive Project coordinator librarian. Rich Dana earned his MFA from the University of Iowa Center for the Book in 2021 and his MA from the School of Library and Information Science in 2020. He has worked as an art mover, art fabricator andContinue reading “Welcome Rich Dana”
Poems That Just Are
“From the Classroom” is a series that features some of the great work and research from students who visit our collections. Below is a blog by Luke Allan from Dr. Jennifer Burek Pierce’s class “Reading Culture History & Research in Media” (SLIS:5600:0001). Poems That Just Are By Luke Allan In a letter to a friendContinue reading “Poems That Just Are”
The Large Glass finds a home in the International Dada Archive
The following is written by International Dada Curator Timothy Shipe. The latest major acquisition for the International Dada Archive is The Large Glass and Related Works (1967-1968), an impressive collaboration between artist Marcel Duchamp and the Egyptian-born Italian writer and gallery owner Arturo Schwarz. The magnificent set of two large portfolios contains a monograph byContinue reading “The Large Glass finds a home in the International Dada Archive”
In Memory of Dr. Marvin Sackner
The following was written by International Dada Curator Timothy Shipe It is with profound sorrow that we note the passing of Dr. Marvin Sackner on Tuesday, September 29 at age 88, just a few weeks after the opening of this exhibition. For those of us at Iowa, Dr. Sackner will be forever remembered for selectingContinue reading “In Memory of Dr. Marvin Sackner”